Power
Race, U.S. Policies, and Politics
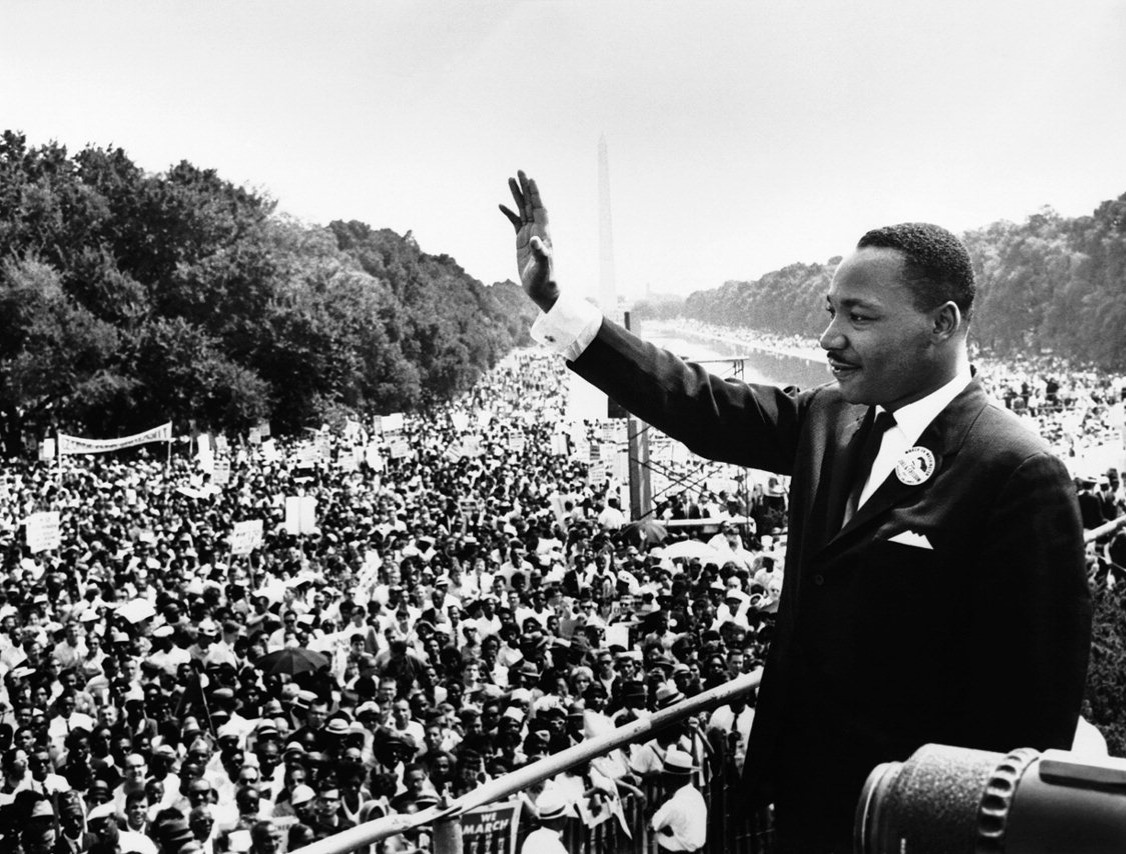
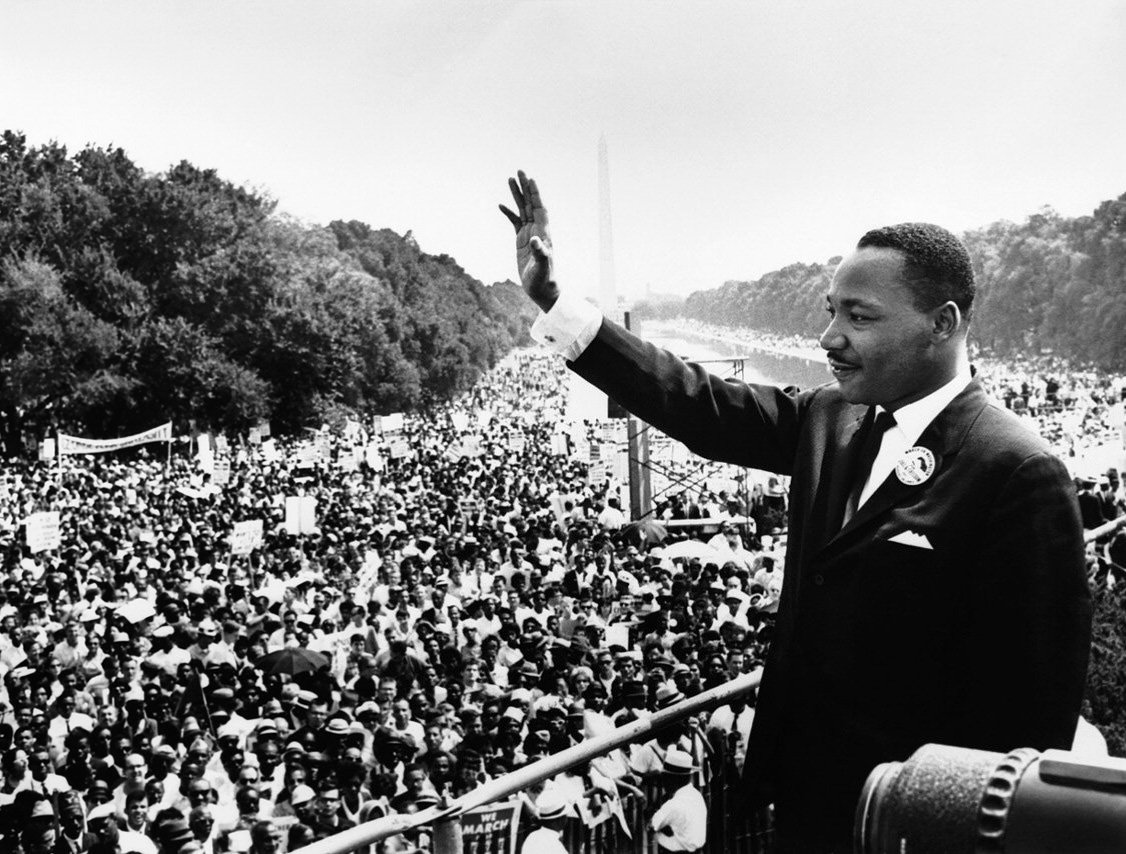
Photograph: Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. giving his "I Have a Dream" speech at the March on Washington on August 28, 1963. Photo credit: Unknown | Public Domain, Wikimedia Commons.
Introduction
The following resources examine how race has played a major role in United States politics and policymaking.
Conversation Stations
These are the images used in artistic physical displays. They are survey questions and conversation starters that are topically and thematically organized. They demonstrate how Jesus is relevant to each topic or theme. You can also just view the images on your device. If you would like, see all our Conversation Stations; below are the ones that relate to the topic of Race.
Whose Justice? (and instructions and Christian Restorative Justice Study Guide)
Whose Justice? for Harvard Law School
Is a Good Friend Hard to Find? (and instructions and conversation tree)
What Can We Do About Evil? (and instructions and conversation tree) and smaller version and brochure version
Que Podemos Hacer Sobre La Maldad? for the Asociacion Dominicana de Estudiantes Evangelico, 2014
Does the Good Outweigh the Bad? (and instructions)
Race What's the Problem? (and instructions) and brochure version
Messages and Resources on Race and Politics
Slides of a presentation given to the 2022 Reconstruction class. The introduction features John Winthrop vs. Roger Williams to highlight the debate over freedom of religious Conscience vs. Christendom. The presentation highlights Christian accomplishments in health and hospitals, education and schools, land ownership and economic justice, and criminal justice reform.
A series of blog posts where we explore how Christian (mostly Protestant) heresies started and continue to influence our modern political and racial challenges. This includes the very notion of race itself, and how our modern economics, housing, schooling, and policing systems have been shaped. Christians must take responsibility for these heresies in the framework of repentance. We have designed a study guide to accompany the blog posts. Please consider using it for personal reflection or discussion in your family, church, organization, etc.
Today’s Christian pro-life movement has misplaced its priorities. The issue of abortion is more complex than the movement often appreciates. For a start, Scripture is less clear about the moral weight of the fetus than we often think. In fact, early Christians took different positions on abortion because they also relied on different scientific sources about the unborn. Furthermore, Christian conservatives today do not acknowledge that in American history, as today, Christian stances on abortion were motivated by other political fears: White Protestant Americans developed different state laws on abortion to accomplish anti-immigrant goals in the North, but anti-black racism in the South. That messiness impacts U.S. constitutional law, including Roe v. Wade. Meanwhile, Scripture commissions God’s people to confront socio-economic factors that push abortion rates higher: male privilege and the disempowerment of women; the high cost of childraising; the causes of birth defects; the desire to care narrowly for just “my children”; mistaken views about contraception and the “culture wars”; and most of all, poverty. The Study and Action Guide to Abortion Policy distills Mako’s book down to three sessions, with some readings and videos.
Atonement, Justice, and Scapegoating
These blog posts relate to both the topic of atonement and the topic of desire because, like fallen Adam in the garden, we desire to deflect blame, and therefore we scapegoat others. On the political level, this builds group cohesion and creates a social outsider, who is blamed for the group’s woes, who the group must exile or kill or marginalize in order to maintain a hopeful lie. This series explores what political scapegoating has looked like in the U.S.
White American Evangelical Political Attitudes and Behavior: Explanation and Correctives
White American evangelical political attitudes can be characterized by the debate between John Winthrop and Roger Williams, and their respective attitudes towards Native Americans, slavery, fairness, and faith in civic space. This is a presentation also explores Scripture and church history to argue that Roger Williams was correct. Given to the staff of Emmanuel Gospel Center, Apr 18, 2018, as a follow-up to how Christian restorative justice impacts ministry; audio file here
The Role of Jesus in Revolution and the Pursuit of Justice
This is an evangelistic message that highlights the Christian-led and Christian-influenced non-violent resistance movements throughout the world in the 20th century. They show the connections and spiritual vitality of Christian faith under empire or empire-like oppression.
Race and Politics: Topics:
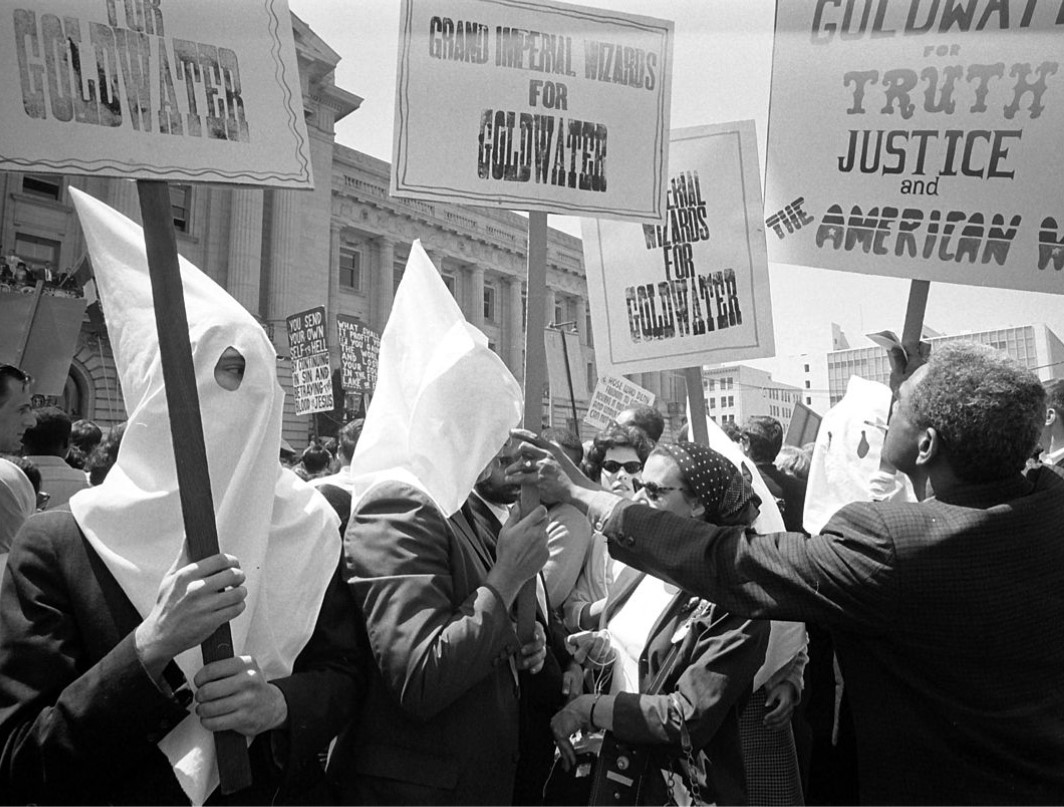
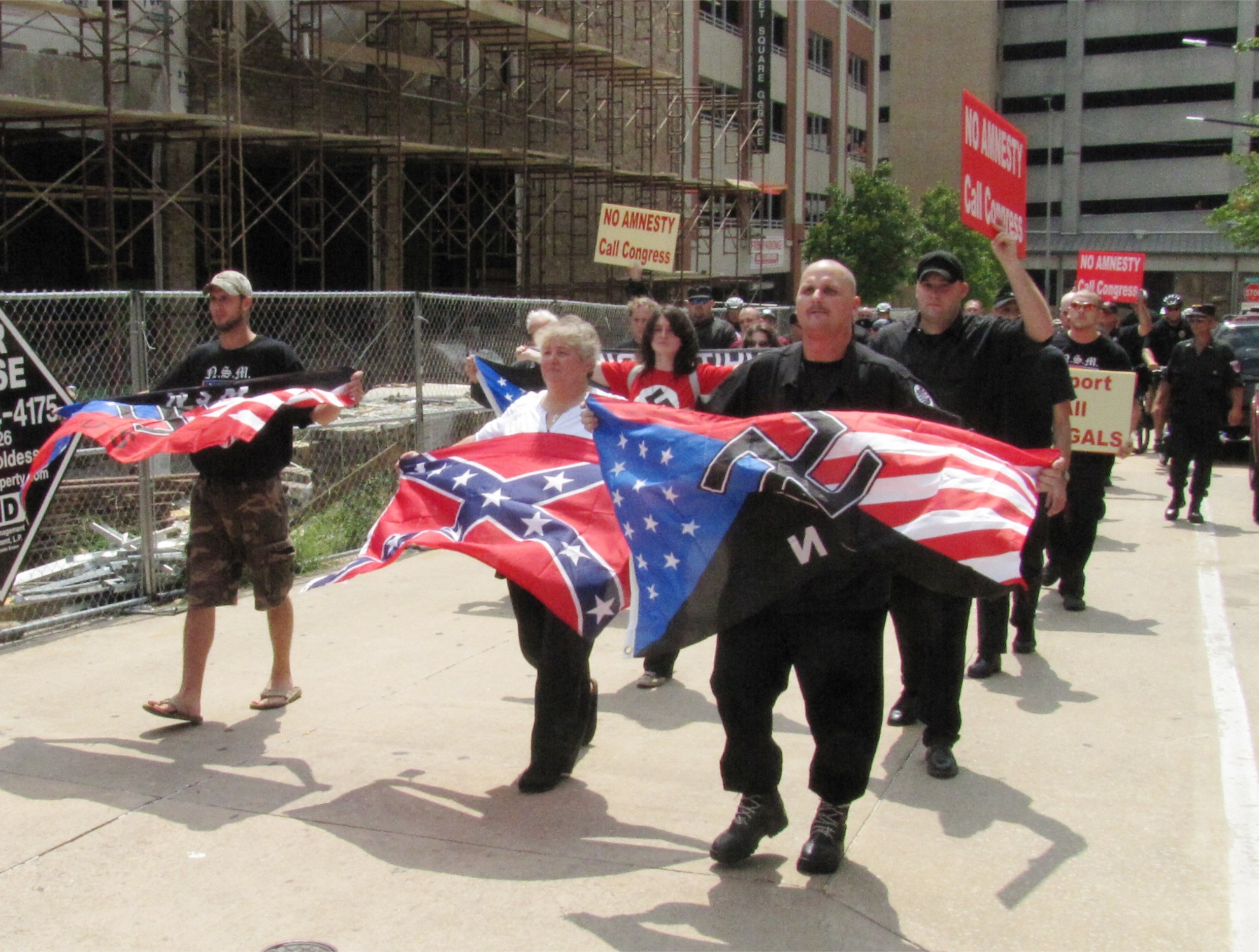
This section, Race and Politics, highlights how race has been used in Political Campaigns as dogwhistles, overtly, or as a wedge issue. Procedural Justice tracks issues like voting rights and districting how race is a factor in upholding or denying them. Substantive Justice spotlights how public investments are influenced by racialized perceptions. Racial Fascism in the U.S. surveys how racial fascism has been organized and continues to be. White Supremacy traces how white supremacy has been negotiated through four major time periods in U.S. history.
Race: Topics:
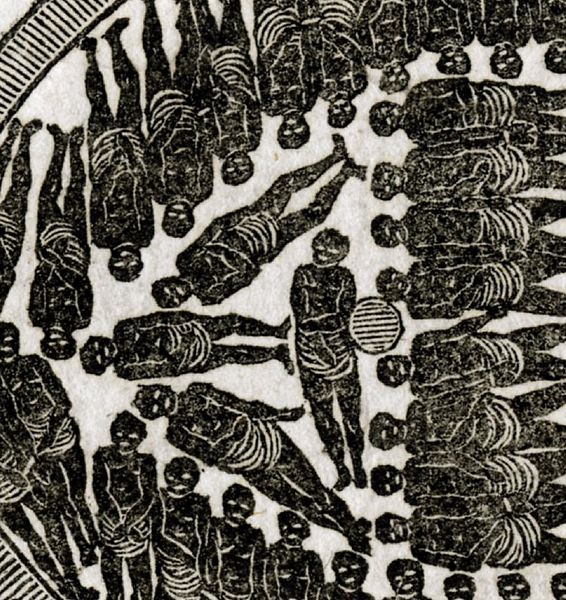
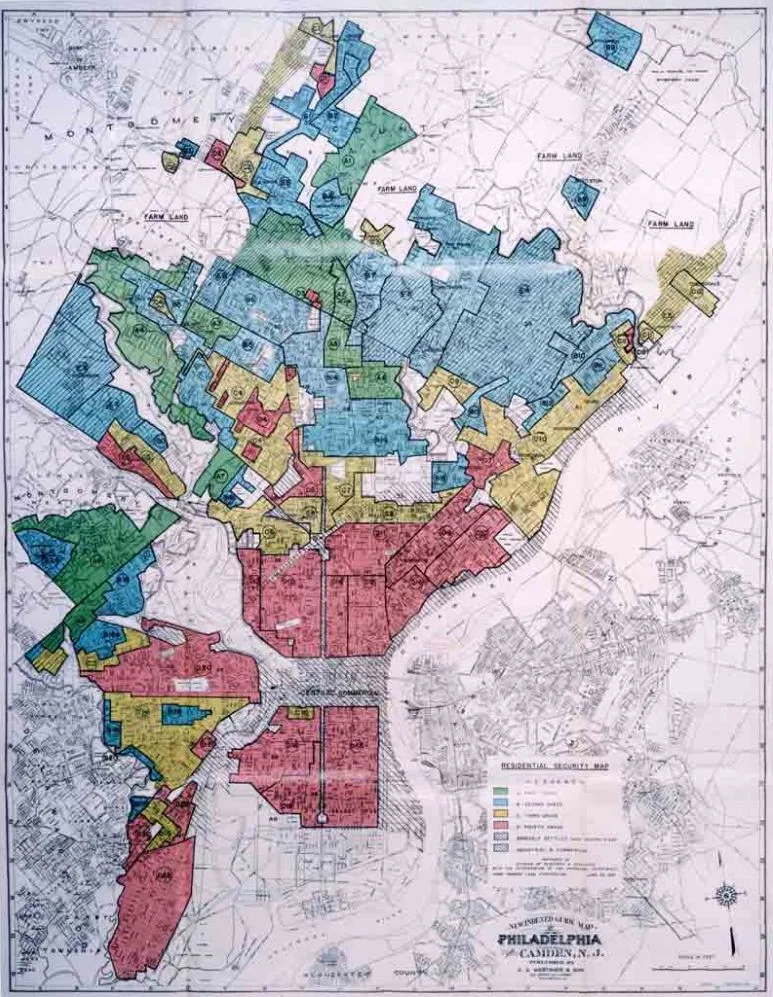
This page is part of our section on Race, which contains the following: Slavery examines the intersections of religious beliefs and slavery, both in the U.S. and elsewhere during colonialism. Land explores Native American land seizure, white supremacy in housing, gentrification, and environmental racism. Finance spotlights racial discrimination in access to capital. Criminal Justice highlights historical racism not only in disparities but practices like convict-leasing, lynching, and hate crimes. Employment lists forms of discrimination in the workplace, hiring, labor unionizing and participation. Eugenics traces the history of eugenics in white American and elsewhere. Schooling examines disparities in the educational system and racial impacts of funding and administration. Power examines the use of race in political campaigns, the procedural justice wrongs such as voting rights denied and gerrymandering, substantive justice wrongs like education, health, and welfare, and racial fascism in the U.S. Immigration examines the moral, economic, and political challenges of immigration, along with the political manipulation of immigration as an issue. Child Development highlights racial implications in emotional development and psychological awareness. Health examines the significance of race disparities from epigenetic factors, environmental factors, medical treatment, and health care politics. Beauty examines how race impacts notions of beauty and professionalism. Race is part of our critique of the political Right and Left in the U.S.
Christian Restorative Justice Critique of the Right: Domestic Policy Topics:
This page is part of our section Critique of the Right, which engages the following topics:
Church and Empire: Topics:
Race is a construct created by European colonialism. For more background, consider the Church and Empire section of our website. This section reminds us what Christian faith was like prior to colonialism, and in resistance to colonialism, to show that Christianity is not “a white man’s religion.”